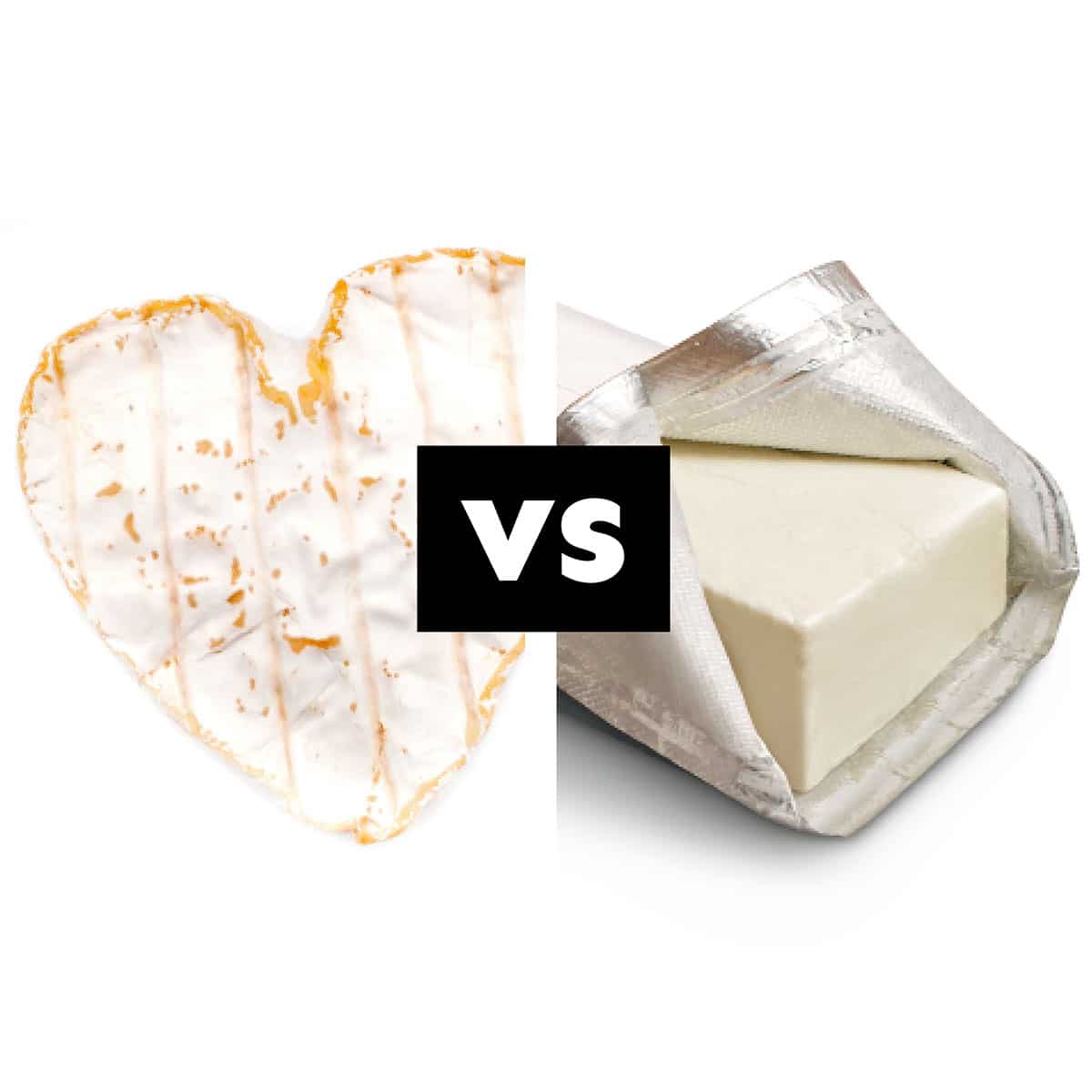
Both creamy and delicious, you may be wondering what the difference between Neufchâtel and cream cheese is (after all, in most supermarkets they come in almost identical packaging!). Neufchâtel has a lower fat content than cream cheese, and can be used in many of the same ways. Read on to learn about its unique uses and flavor!
Origin and History
Neufchâtel Cheese: Reverently referred to as “the heart of Normandy,” Neufchatel has its origins in the Neufchâtel-en-Bray region of Normandy, France. Its history dates back to at least the 6th century making it possibly the oldest French cheese. Legend has it that during the Hundred Years’ War, French farm girls made heart-shaped Neufchâtel cheeses as a token of affection for English soldiers.
France has given Neufchâtel an AOC (appellation d’origine contrôlée) which means “controlled designation of origin,” and is given by the Institut national de l’origine et de la qualité (INAO). Think of it as a patent but for cheese.
Cream Cheese: The origin of cream cheese couldn’t be more different than Neufchatel cheese. Cream cheese was invented in Chester, New York by Mr William Lawrence in 1872. He knew he was on to something good, so he bought an existing cheese factory and commercialized the creamy spread we love today.
Lawrence’s creation was marketed as “Philadelphia Cream Cheese,” and the name “Philadelphia” became synonymous with cream cheese, despite the fact that it wasn’t necessarily made in the city of Philadelphia. The product gained popularity quickly and became a staple in American cuisine.


How Neufchatel and Cream Cheese are Made
Neufchâtel Cheese: This is a soft mold-ripened cheese typically made from cow’s milk, which is curdled using either lactic acid or rennet. The curd is then cut, drained, and molded into various shapes, with the traditional heart shape being the most iconic. The cheese is given six to eight weeks to mature and ripen into a soft cheese, and to develop its characteristic flavors and textures. Neufchâtel is produced in both artisanal and industrial settings, resulting in variations in taste and quality.
Generally, Neufchatel from France is made only with milk. In the USA it is made from milk and cream. The French varieties are thus lower in fat, and by their standards the cheese must contain between 20% and 33% milk fat and a moisture content of no more than 65%. This makes Neufchatel sort of a “low fat cream cheese”.
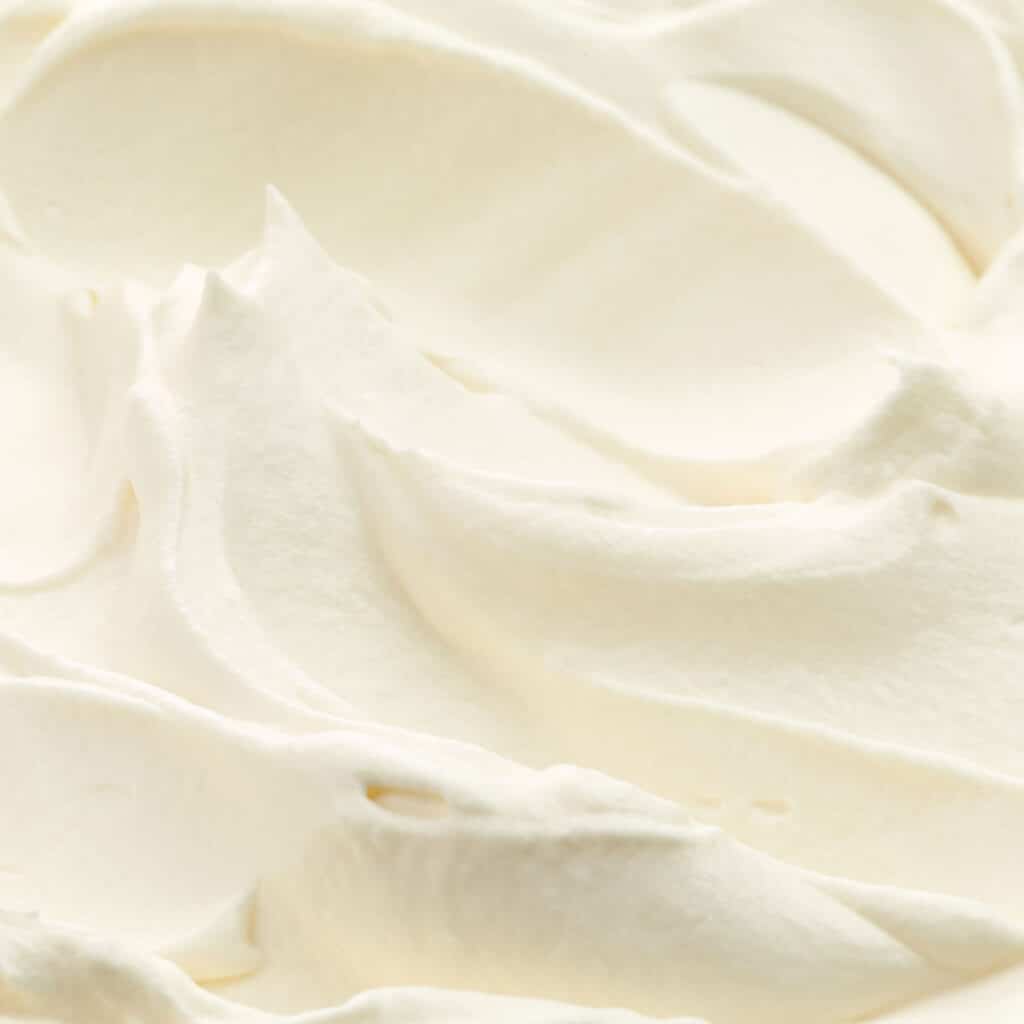
Cream Cheese: Cream cheese is typically made from a mixture of cream and pasteurized milk. Lactic acid is added to form curds. These curds are drained and blended until smooth and creamy. Depending on the desired fat content, additional cream may be added to achieve the desired texture and flavor. Unlike Neufchatel, there is no aging involved.
The FDA got involved in the standards for cream cheese and defines it as having a fat content of at least 33% fat and a moisture content of 55% or less.

Appearance
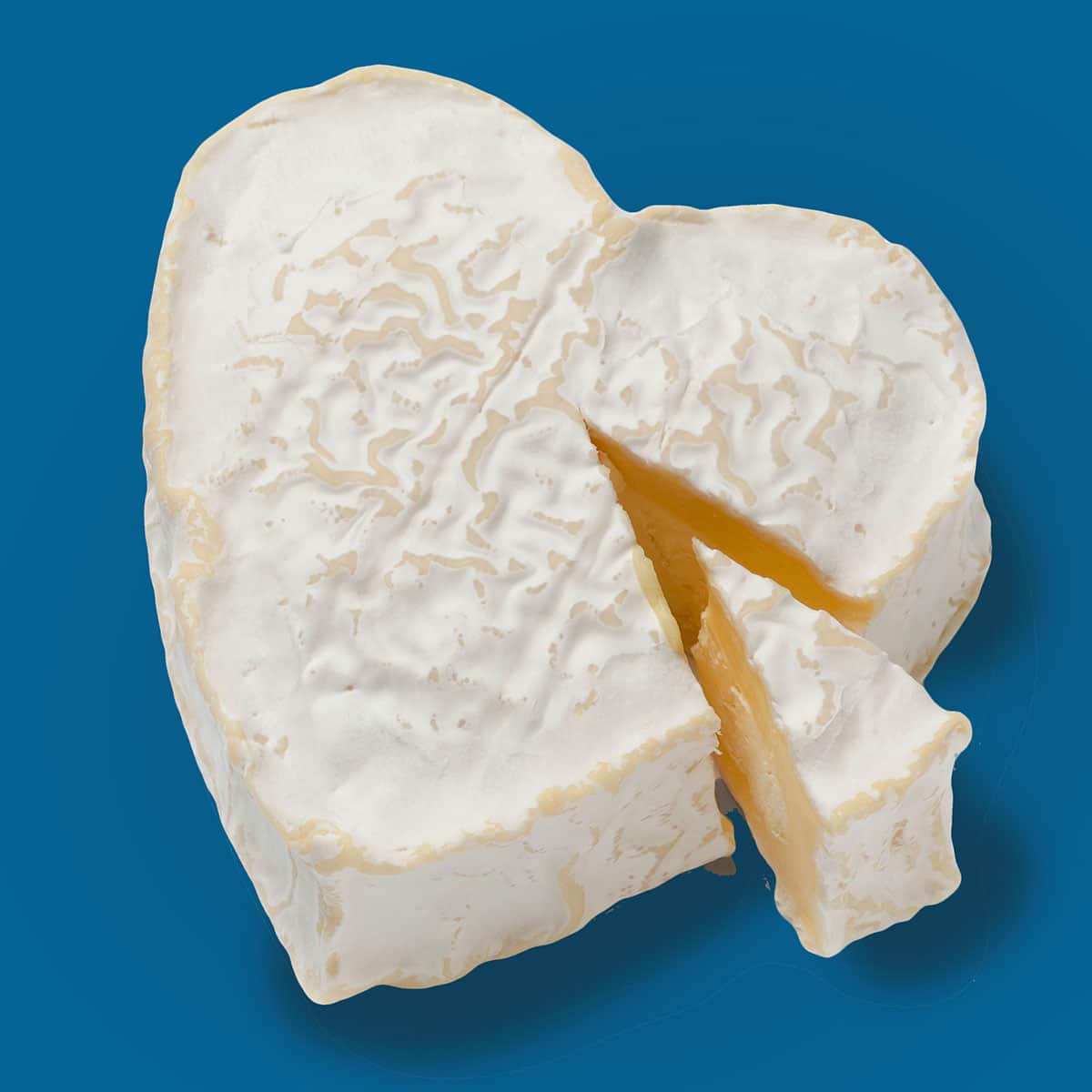
Neufchâtel Cheese Appearance: Neufchatel can be found in different shapes, with the heart shape being the most recognizable. It looks very similar to brie or camembert and has the same firm white edible rind. Neufchatel has a pale, slightly crumbly outer layer, which gradually becomes smoother and creamier toward the center as it ripens. When young, it has a white, bloomy rind that forms due to the growth of mold on the surface.
Cream Cheese Appearance: Cream cheese is known for its smooth and velvety appearance. It is typically ivory or pale white in color, although variations exist based on the specific ingredients used and any added flavors. When properly prepared, cream cheese has a consistent texture without any lumps or graininess.
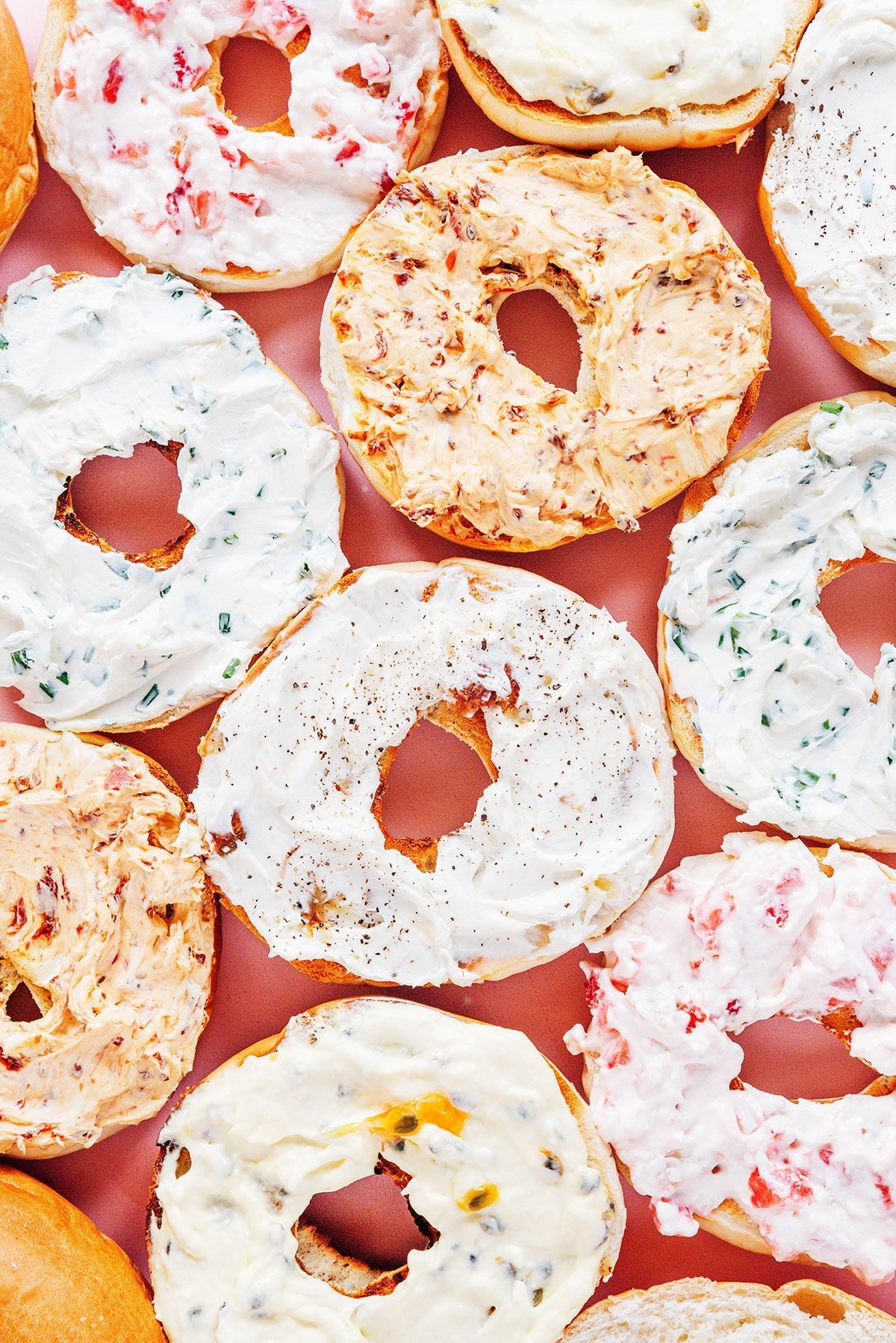

Flavor and Texture
Neufchatel: The flavor of Neufchâtel cheese can vary depending on its age. When young, it possesses a mild and tangy taste with subtle earthy notes. As it matures, the flavors intensify, becoming richer, more pungent, and more savory. It has a sharper taste than its similar cousins (brie or camembert), and has a grainy texture vs brie’s creamy texture.
Cream Cheese: Cream cheese boasts a mild and slightly tangy flavor profile, owing to the acidification process. Its texture is luxuriously creamy, smooth, and spreadable. This makes it ideal for spreading on bagels, crackers, and sandwiches. The richness of cream cheese also makes it a popular ingredient in various sweet and savory dishes.
Neufchâtel and cream cheese are similar in flavor, but Neufchâtel tastes a bit tangier with a grainier texture. Neufchâtel also has an edible rind that gives a more pungent flavor.
Culinary Uses
Neufchâtel Uses: This is a versatile cheese that can be used in a variety of culinary applications. It’s often spread on crackers, bread, or bagels due to its creamy texture and pleasant tanginess. The cheese also adds depth and creaminess to sauces, dips, and soups. In desserts, Neufchâtel can be incorporated into cheesecakes, tarts, and pastries to provide a velvety texture.
Cream Cheese Uses: Cream cheese has an extensive range of culinary applications. It is often used as a spread for bagels, toast, and crackers. It serves as a key ingredient in many desserts, including cheesecakes, frostings, and creamy fillings for pastries or strawberry stuffed french toast. Cream cheese can also be incorporated into savory dishes like dips, sauces, and creamy pasta dishes to add depth and richness. It’s versatile enough to be blended with herbs, spices, fruits, or other flavorings to create a wide array of flavor variations. You can easily make your own home flavored cream cheese.
Cream cheese’s higher fat content generally makes it the better option for cooking, but this isn’t a hard rule. Recipes that involve melted cream cheese won’t come out as well with Neufchatel as its lower fat content will not provide as smooth a melt as you will get from cream cheese. The added fat of cream cheese also makes it a better choice as a thickening agent for soups or sauces.
Storage
Storing Neufchatel: To ensure the freshness and quality of neufchâtel cheese, it’s important to store it properly. It should be kept in its original packaging or wrapped tightly in plastic wrap to prevent it from drying out. It’s best to store it in the refrigerator’s dairy compartment where the temperature is slightly higher and humidity is controlled. Consume it within 1-2 weeks to enjoy its best flavors and textures. Neufchatel lasts longer than cream cheese, but not as long as many other Types of Cheese.
Storing Cream Cheese: Cream cheese is perishable and has a short shelf life once opened. It should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain its freshness and quality. Unopened packages can last for 3-4 weeks or more, but once opened, it’s best to consume or use it within 1 to 2 weeks to prevent spoilage. To prolong its shelf life, it’s advisable to store cream cheese in an airtight container and avoid exposing it to excessive moisture.
Varieties
Varieties of Neufchatel: There are a few different varieties and types of Neufchâtel cheese:
- French Neufchâtel: This is the original variety, hailing from Normandy, France. It’s traditionally molded into the shape of a heart and aged for 6-8 weeks. The cheese has a bloomy rind and a creamy interior.
- American Neufchâtel: In the United States, Neufchâtel cheese is often used as a lower-fat alternative to cream cheese. While the French version has a fat content of around 40%, American neufchâtel cheese contains about 23% fat. It’s commonly used in cooking and baking, as well as for spreading on bagels and crackers.
- Flavored Varieties: Neufchâtel cheese can also come in various flavored versions, much like cream cheese. These flavors can range from savory options like herbs and spices to sweet versions with fruits or chocolate.
When choosing Neufchâtel cheese, it’s important to consider the specific variety and its intended use. If you’re looking for a spreadable cheese with a lower fat content, American Neufchâtel cheese might be a good choice. On the other hand, if you’re interested in experiencing the traditional French version, look for the heart-shaped cheeses with a bloomy rind.
Varieties of Cream Cheese:
Original Cream Cheese: This is the classic variety of cream cheese that most people are familiar with. It has a rich and creamy texture, a mildly tangy flavor, and is often used as a spread on bagels, crackers, and bread. It’s also a common ingredient in cheesecakes and other desserts.
- Whipped Cream Cheese: Whipped cream cheese is the same as the original variety, but it’s been whipped to incorporate air. This results in a lighter and fluffier texture. It’s easier to spread and is often used in recipes where a smoother consistency is desired.
- Flavored Cream Cheese: Many brands offer cream cheese with added flavors, created by herbs, spices, fruits, vegetables, or even chocolate. These flavored varieties can add an extra dimension of taste to your dishes, whether you’re spreading it on a bagel or using it in recipes. If you want to make your own home flavored cream cheese it is really pretty easy.
- Reduced-Fat or Low-Fat Cream Cheese: These varieties have a lower fat content compared to traditional cream cheese. They are made by using less cream in the mixture, which results in a lighter texture and fewer calories. However, they might have a slightly different taste and texture compared to full-fat cream cheese.
- Vegan Cream Cheese: With the rise in popularity of plant-based diets, there are now cream cheese alternatives made from ingredients like nuts (such as cashews), soy, or other plant-based sources. These vegan options aim to replicate the flavor and texture of traditional cream cheese without using any animal products.
When selecting cream cheese, consider your intended use. Original cream cheese is versatile and can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, while flavored varieties can add exciting twists to your recipes. Reduced-fat or vegan options are great for those looking to reduce their fat intake or follow specific dietary restrictions. Always check the label for nutritional information and ingredient lists to find the best cream cheese for your needs.
Neufch
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cream cheese spread vs cream cheese? You will occasionally see a product called cream cheese spread. It is less regulated, and made with stabilizers and emulsifiers making it less dense and more spreadable.
Is cream cheese cheese? Absolutely! It doesn’t have the savory flavor of say a colby or swiss cheese, in part because it isn’t aged and can be called a fresh cheese. It is still definitely a cheese.
Is Neufchatel cream cheese a type of cream cheese? There is no Neufchatel cream cheese. Neufchatel is just so similar to cream cheese, some people mistakenly call it this.
This wraps up our comparison of cream cheese vs Neufchatel cheese. We hope you found information you can use, and if you are interested in some other variety of cheese check out our comprehensive 53 Types of Cheese. And, as always, happy cooking!




Leave a Comment